Rheumatic Arthritis
What is Rheumatic Arthritis?
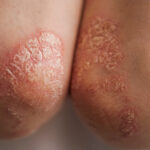
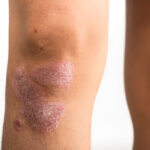
Rheumatic Arthritis, commonly known as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), is a chronic autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and joint damage. It primarily affects the small joints of the hands and feet but can involve multiple systems and organs over time. Unlike osteoarthritis, RA affects the joint lining, leading to painful swelling and, if left untreated, can result in joint deformity and bone erosion.
Symptoms of Rheumatic Arthritis
Persistent joint pain, swelling, and stiffness
Morning stiffness lasting more than 30 minutes
Symmetrical joint involvement (both sides of the body)
Fatigue and general malaise
Low-grade fever
Weight loss
Deformities in advanced stages (e.g., ulnar deviation)
Causes of Rheumatic Arthritis
Autoimmune response where the immune system attacks joint tissues
Genetic susceptibility (family history of RA)
Environmental triggers (e.g., smoking, infections)
Hormonal factors (more common in women)
Age (commonly begins between ages 30 and 60)